Pseudomonas luteola en hurones
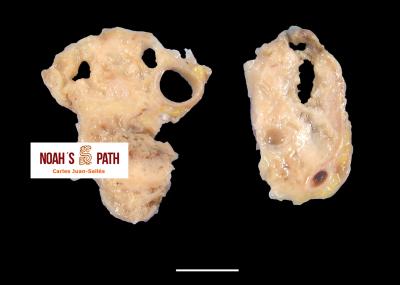
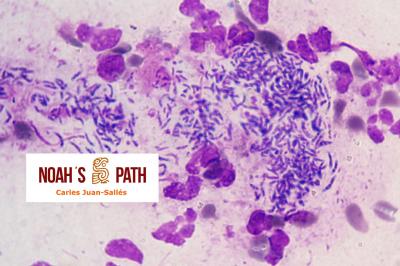
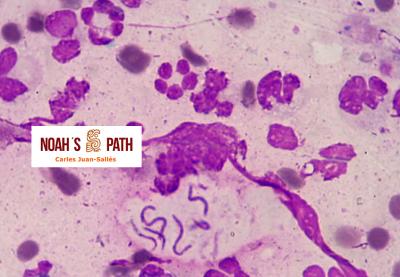
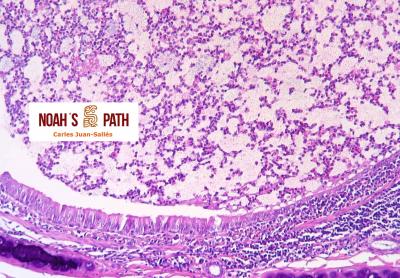
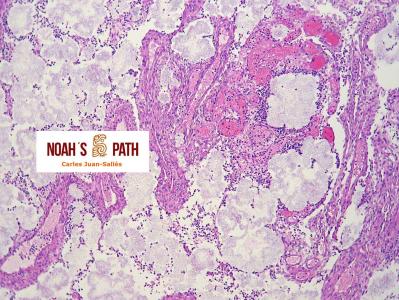
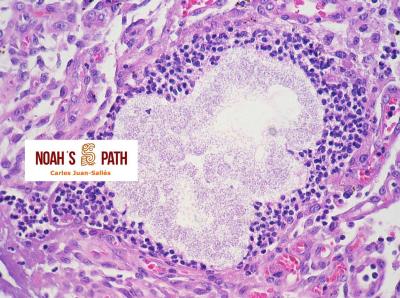
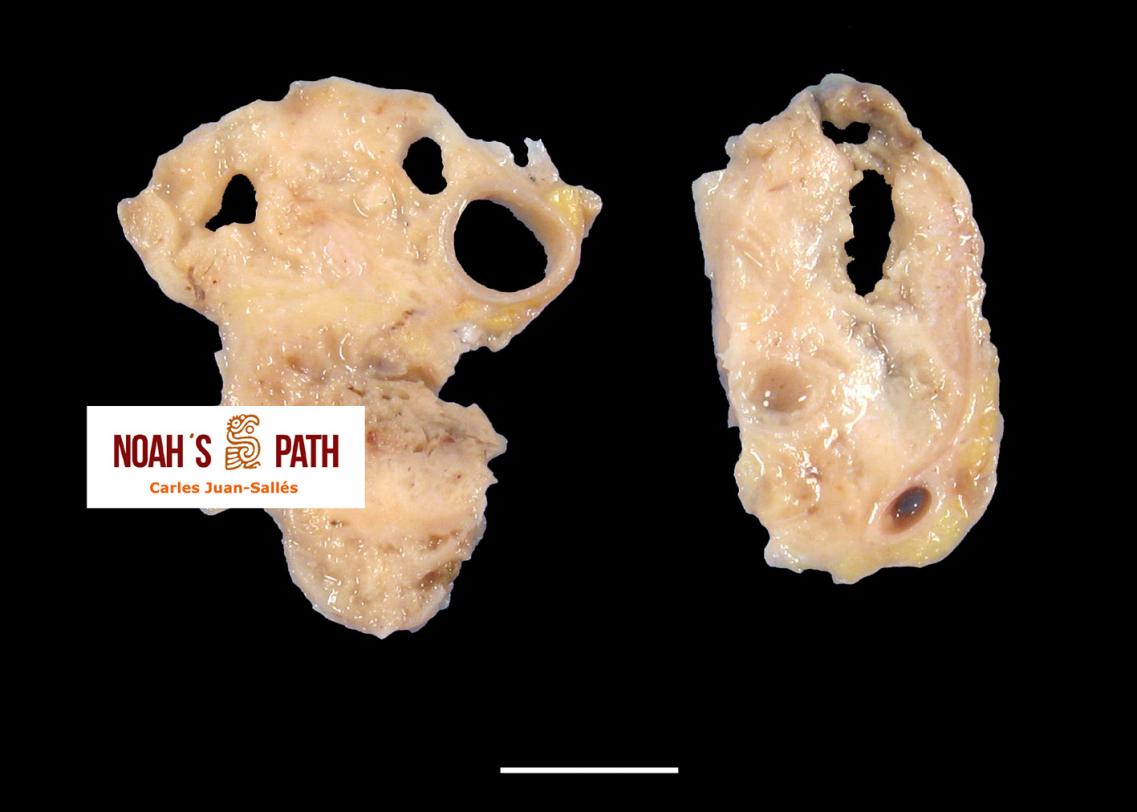
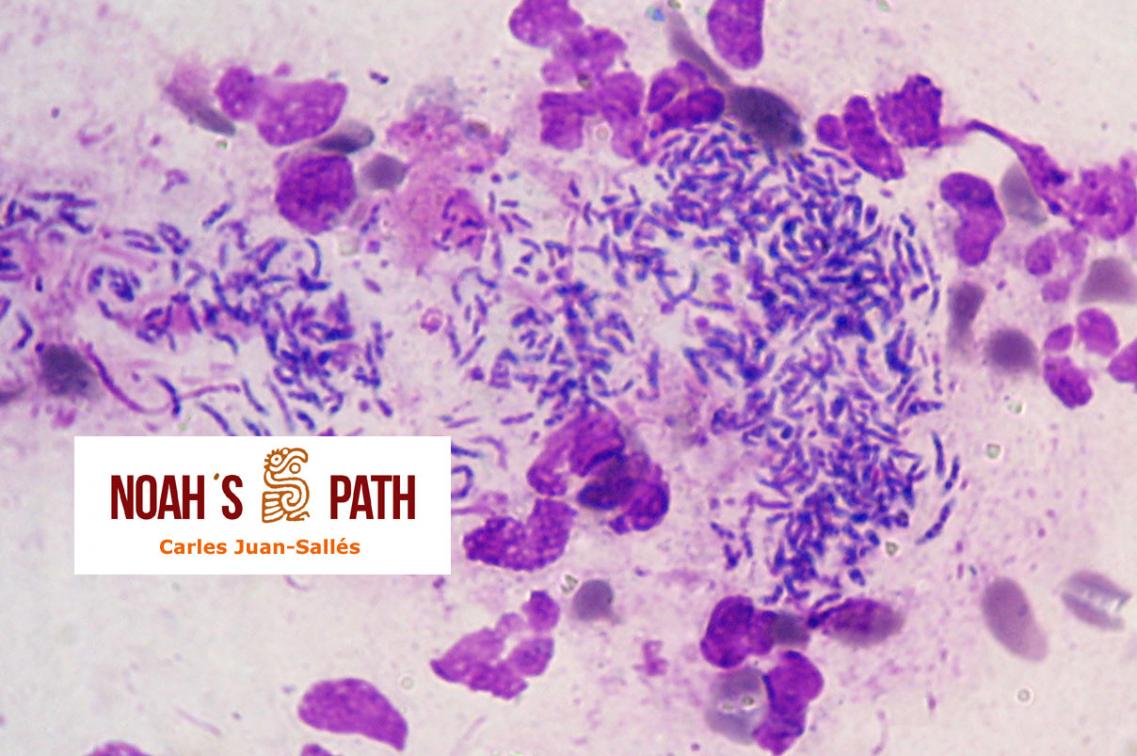
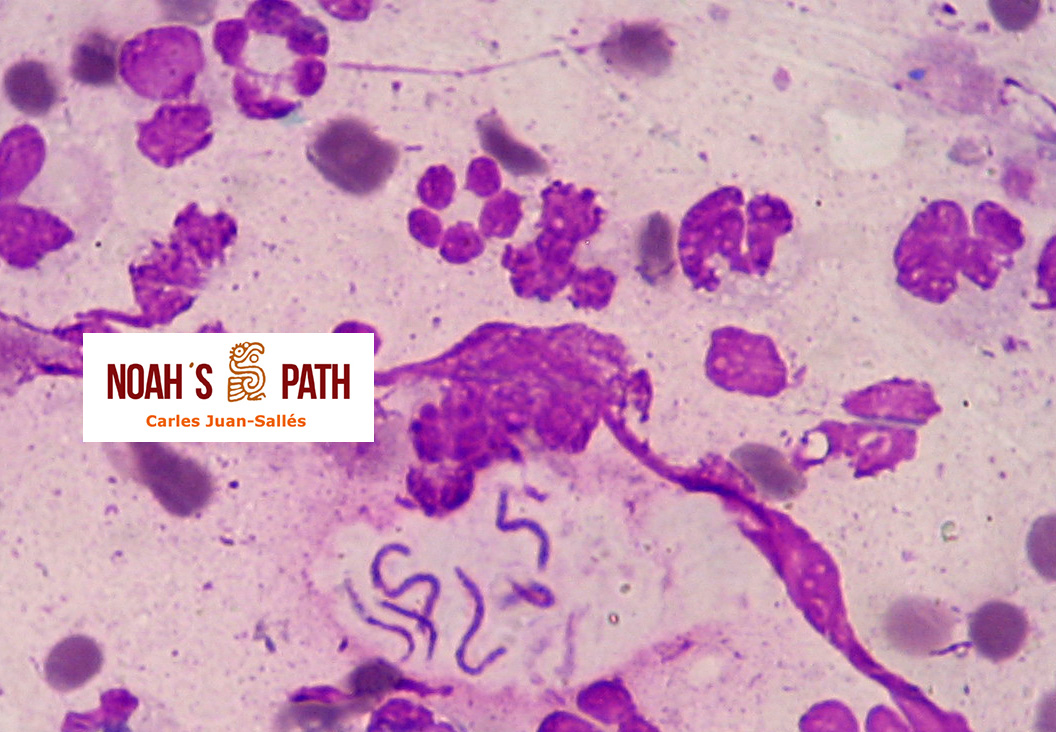
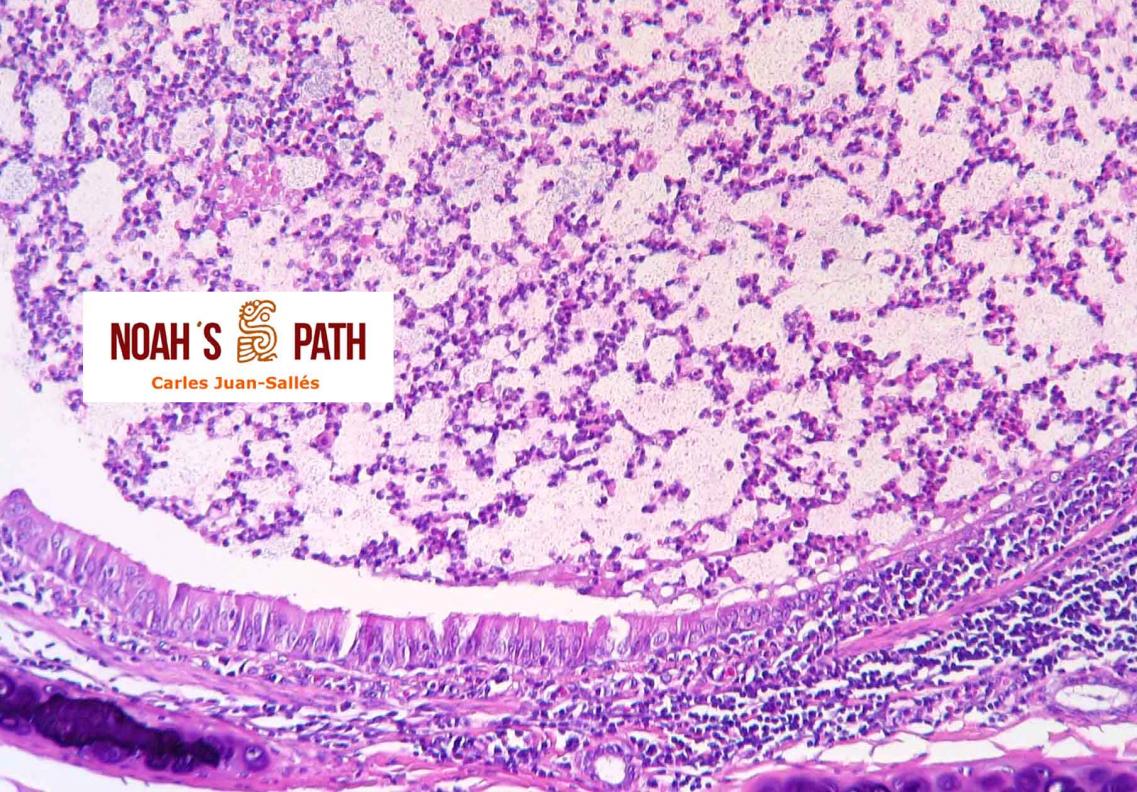
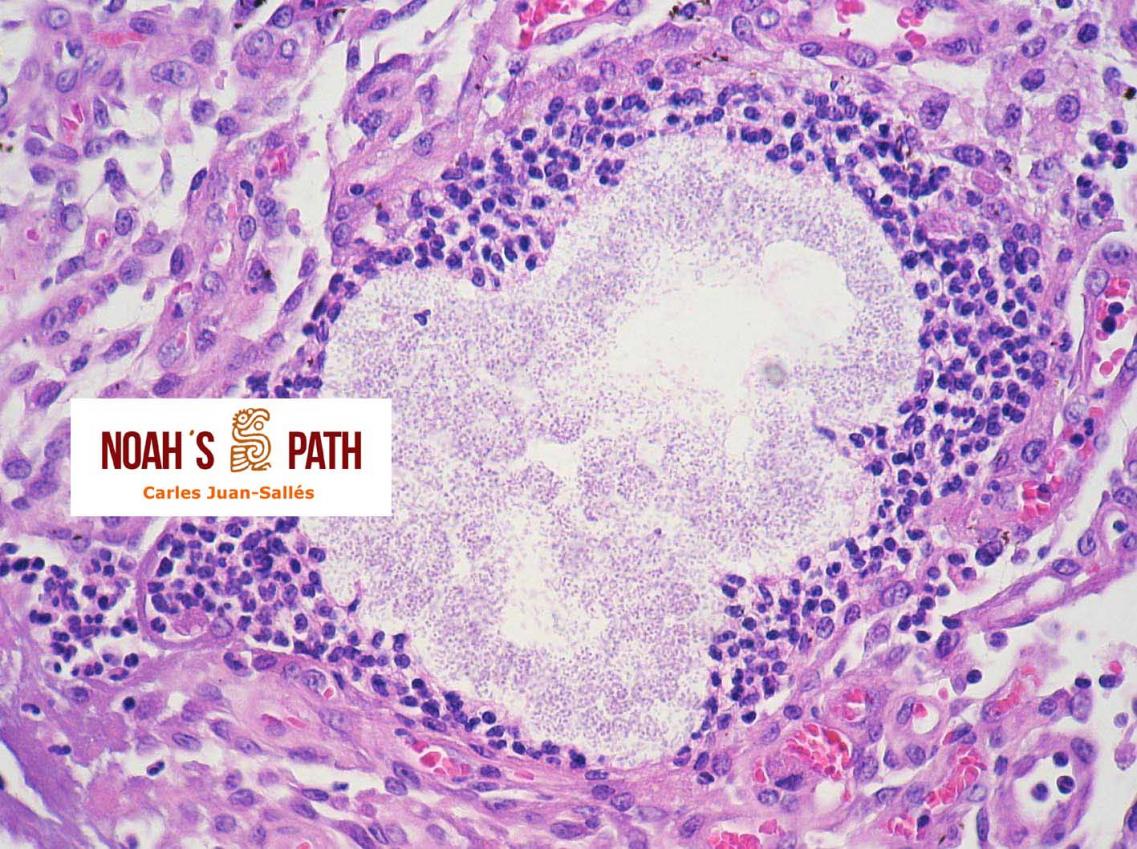
Diagnosticando el caso índice e iniciando en 2008 el primer estudio de una nueva infección bacteriana emergente de los hurones: Pseudomonas luteola. Inicialmente identificado como patógeno con predilección por el mediastino y órganos torácicos (piotórax, bronconeumonía, pleuritis, mediastinitis/masas mediastínicas) en hurones, estudios recientes indican que P. luteola es además causa relevante de abscesos y piogranulomas subcutáneos en diversas localizaciones e incluso intra-abdominales en esta especie. Desde los casos iniciales, en Noah's Path hemos diagnosticado 5 adicionales, 3 con infecciones torácicas y 3 subcutáneas (1 caso padecía una infección mixta). Esta bacteria puede causar infecciones en pacientes humanos (particularmente nosocomiales).
Publicaciones/presentaciones en congresos: Martínez J, Martorell J, Abarca ML, Olvera A, Ramis A, Woods L, Cheville N, Juan-Sallés C, et al: Pyogranulomatous pneumonia and mediastinitis in ferrets (Mustela putorius furo) associated with Pseudomonas luteola infection. Journal of Comparative Pathology, 146:4-10, 2012. Máinez M, Rosell J, Cardona T, Juan-Sallés C: Absceso submandibular por Pseudomonas luteola en un hurón sin enfermedad pleuropulmonar/mediastínica. Resumen 00309 (CD ponencias, XIV Congreso de Especialidades Veterinarias de AVEPA. Toledo, España, 10-11/04/2015).